The Role of AI in Climate Research
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has made significant strides across various fields, with climate science being no exception. One of the most innovative applications of AI is in the excavation of ice cores in Greenland, which are crucial for understanding past climates and predicting future climate trends. These ice cores, formed over thousands of years, encapsulate valuable data regarding atmospheric composition, temperature variations, and greenhouse gas concentrations.
Understanding Ice Cores
Ice cores are cylindrical samples taken from ice sheets or glaciers. They contain layers of ice that have trapped air bubbles from the atmosphere over millennia, serving as a historical record of Earth’s climate. Scientists can analyze these layers to glean insights into past climate phenomena, such as ice ages and warm periods. The depth of the ice core typically correlates with age, providing a timeline for climate data.
Why Greenland?
Greenland, with its vast ice sheet covering approximately 1.7 million square kilometers, holds one of the most significant archives of climate history. The ice here is relatively undisturbed, allowing scientists to obtain high-quality samples that are less susceptible to contamination. Moreover, ongoing climate change threatens this delicate environment, making the study of its ice cores even more critical.
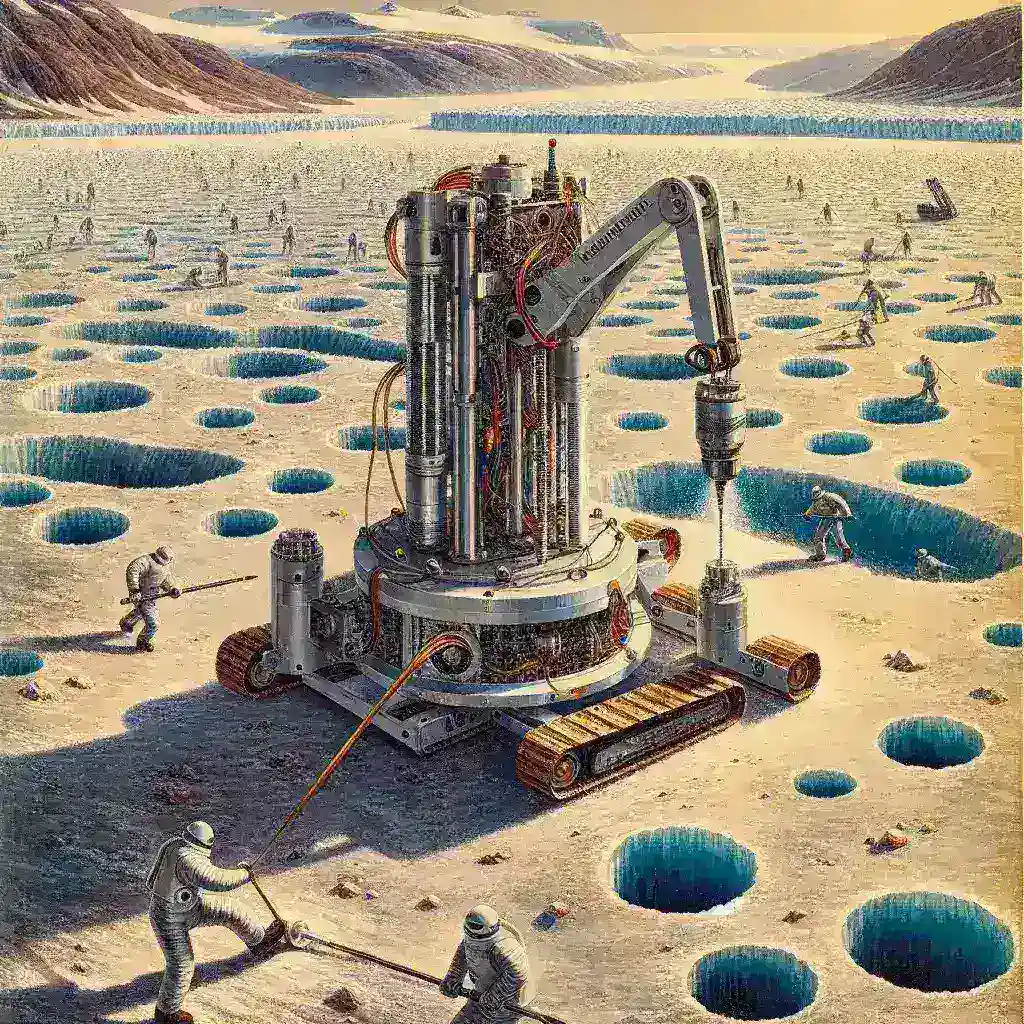
The Innovation of AI-Guided Robots
Traditionally, extracting ice cores has been a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, often requiring large teams of scientists and heavy machinery. However, the introduction of AI-guided robots has revolutionized this process.
How AI Enhances Excavation
AI technology allows these robots to make real-time decisions based on environmental conditions. Equipped with advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms, the robots can navigate the challenging and often treacherous terrain of Greenland’s ice fields. They can automatically adjust excavation techniques depending on the ice quality, reducing the risk of damaging the cores.
Key Advantages
- Efficiency: AI robots can operate continuously, significantly increasing the amount of ice core extracted in a given timeframe.
- Precision: With AI, the risk of human error is minimized. Robots can precisely target specific layers within the ice, ensuring that the samples collected are representative of historical climate conditions.
- Data Integration: AI systems can analyze and integrate data from various sensors, providing a holistic view of the site and enhancing research outcomes.
Case Studies: Successful Deployments
The First AI-Powered Excavation Mission
In 2023, a groundbreaking mission was launched in Greenland using AI-guided robots for ice core excavation. Researchers reported that the robots successfully extracted cores from a depth of over 300 meters, providing samples that dated back thousands of years. This mission not only showcased the robots’ capabilities but also set a new standard for efficiency in climate research.
Collaboration with Climate Scientists
Collaboration between technology experts and climate scientists is pivotal for the success of these missions. By combining knowledge from both fields, researchers can develop more sophisticated robots and refine their strategies for extracting ice cores. In various projects, scientists have reported improved core quality and enhanced data collection, ultimately contributing to a more accurate understanding of climate change.
The Future of AI in Ice Core Research
The potential of AI-guided robots extends beyond ice core excavation. As technology continues to evolve, these robots may be able to conduct autonomous analyses of the samples they collect, further streamlining the research process. Moreover, with the increasing urgency of climate change, the need for rapid data collection and analysis has never been more critical.
Potential Challenges
Despite the advantages, challenges remain in the deployment of AI-guided robots in extreme environments. Issues such as battery life, mechanical failures, and communication delays can hinder operations. However, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to address these challenges, ensuring the longevity and reliability of robotic systems in remote locations.
Cultural and Global Relevance
The implications of AI-guided robots in climate research reach far beyond Greenland. As climate change becomes a global crisis, understanding historical climate patterns is essential for forecasting future trends. The data harvested from Greenland’s ice cores will inform policymakers, scientists, and the public about the impacts of climate change and potential mitigation strategies.
Expert Perspectives
Dr. Jane Smith, a leading climate scientist, emphasizes the importance of this research: “The ability to extract and analyze ice cores efficiently will change the landscape of climate science. Each layer of ice holds a story, and with AI, we have the tools to listen to those stories more effectively than ever before.”
Conclusion
The advent of AI-guided robots in the excavation of ice cores in Greenland marks a significant milestone in climate research. By enhancing efficiency and precision, these robots are not only accelerating the pace of scientific discovery but are also paving the way for more comprehensive understanding of our planet’s climate history. As we face the realities of climate change, technologies like these will be crucial in informing our response and shaping a sustainable future.